Troubleshooting#
How to SSH to the machine#
First make sure your SSH key has been deployed to the server. See Adding the public SSH key to the server for more details.
Once the key is set up, connect to the machine over SSH using the following command:
ssh ubuntu@51.178.95.143
Looking at logs#
See: The Littlest JupyterHub documentation.
The main components to have a look at are:
the JupyterHub instance
Traefik (proxy)
the user server
The logs for the hub and proxy can be inspected with:
sudo journalctl -u jupyterhub
sudo journalctl -u traefik
Note
To follow the logs of the services and print more content on the screen, you can combine the
-f (print the end and follow new logs) and -n (specify the number of lines to display) options:
sudo journalctl -u jupyterhub -f -n 1000
If you want a clean restart of these services, run:
sudo systemctl restart jupyterhub
sudo systemctl restart traefik
In Plasma, the user servers run in Docker containers. To access the logs of a particular server, first identify the name of the user.
Then run:
# list all the containers
docker ps
# use -f to follow the logs
docker logs -f jupyter-username
The logs will look like the following:
$ docker logs -f jupyter-alice
[I 2022-03-09 08:42:40.322 SingleUserNotebookApp notebookapp:1593] Authentication of /metrics is OFF, since other authentication is disabled.
[I 2022-03-09 08:42:40.856 LabApp] JupyterLab extension loaded from /usr/local/lib/python3.9/site-packages/jupyterlab
[I 2022-03-09 08:42:40.856 LabApp] JupyterLab application directory is /usr/local/share/jupyter/lab
Patching auth into jupyter_server.base.handlers.JupyterHandler(jupyter_server.base.handlers.AuthenticatedHandler) -> JupyterHandler(jupyterhub.singleuser.mixins.HubAuthenticatedHandler, jupyter_server.base.handlers.AuthenticatedHandler)
[I 2022-03-09 08:42:40.864 SingleUserNotebookApp mixins:576] Starting jupyterhub-singleuser server version 1.5.0
[I 2022-03-09 08:42:40.867 SingleUserNotebookApp notebookapp:2329] Serving notebooks from local directory: /home/jovyan
[I 2022-03-09 08:42:40.867 SingleUserNotebookApp notebookapp:2329] Jupyter Notebook 6.4.8 is running at:
[I 2022-03-09 08:42:40.867 SingleUserNotebookApp notebookapp:2329] http://4aace966ddb0:8888/user/alice/
[I 2022-03-09 08:42:40.867 SingleUserNotebookApp notebookapp:2330] Use Control-C to stop this server and shut dow
If the user servers have stopped, logs can still be accessed via journald:
sudo journalctl CONTAINER_NAME=jupyter-username-
The logs will look like the following:
-- Logs begin at Tue 2022-03-01 05:32:13 UTC, end at Tue 2022-03-29 07:04:03 UTC. --
Mar 29 07:02:13 plasmabio-test 1237fbae7d24[23293]: [I 2022-03-29 07:02:13.162 SingleUserNotebookApp notebookapp:1593] Authentication of /metrics is OFF, since other authentication is disabled.
Mar 29 07:02:14 plasmabio-test 1237fbae7d24[23293]: [I 2022-03-29 07:02:14.011 LabApp] JupyterLab extension loaded from /srv/conda/envs/notebook/lib/python3.7/site-packages/jupyterlab
Mar 29 07:02:14 plasmabio-test 1237fbae7d24[23293]: [I 2022-03-29 07:02:14.011 LabApp] JupyterLab application directory is /srv/conda/envs/notebook/share/jupyter/lab
Mar 29 07:02:14 plasmabio-test 1237fbae7d24[23293]: [I 2022-03-29 07:02:14.020 SingleUserNotebookApp extension:22] nteract extension loaded from /srv/conda/envs/notebook/lib/python3.7/site-packages/nteract_on_jupyter
Mar 29 07:02:14 plasmabio-test 1237fbae7d24[23293]: Patching auth into jupyter_server.base.handlers.JupyterHandler(jupyter_server.base.handlers.AuthenticatedHandler) -> JupyterHandler(jupyterhub.singleuser.mixins.HubAuthenticatedHandler, jupyter_server.base.handlers.AuthenticatedHan>
Mar 29 07:02:14 plasmabio-test 1237fbae7d24[23293]: [I 2022-03-29 07:02:14.023 SingleUserNotebookApp mixins:576] Starting jupyterhub-singleuser server version 1.5.0
Mar 29 07:02:14 plasmabio-test 1237fbae7d24[23293]: [W 2022-03-29 07:02:14.030 SingleUserNotebookApp _version:73] jupyterhub version 1.1.0 != jupyterhub-singleuser version 1.5.0. This could cause failure to authenticate and result in redirect loops!
Mar 29 07:02:14 plasmabio-test 1237fbae7d24[23293]: [I 2022-03-29 07:02:14.030 SingleUserNotebookApp notebookapp:2302] Serving notebooks from local directory: /srv/home/foo/test-gist
Mar 29 07:02:14 plasmabio-test 1237fbae7d24[23293]: [I 2022-03-29 07:02:14.030 SingleUserNotebookApp notebookapp:2302] Jupyter Notebook 6.3.0 is running at:
Mar 29 07:02:14 plasmabio-test 1237fbae7d24[23293]: [I 2022-03-29 07:02:14.030 SingleUserNotebookApp notebookapp:2302] http://1237fbae7d24:8888/user/foo/
Mar 29 07:02:14 plasmabio-test 1237fbae7d24[23293]: [I 2022-03-29 07:02:14.030 SingleUserNotebookApp notebookapp:2303] Use Control-C to stop this server and shut down all kernels (twice to skip confirmation).
Mar 29 07:02:14 plasmabio-test 1237fbae7d24[23293]: [I 2022-03-29 07:02:14.035 SingleUserNotebookApp mixins:557] Updating Hub with activity every 300 seconds
Mar 29 07:02:14 plasmabio-test 1237fbae7d24[23293]: [I 2022-03-29 07:02:14.810 SingleUserNotebookApp log:189] 302 GET /user/foo/ -> /user/foo/lab? (@172.17.0.1) 1.28ms
Mar 29 07:02:14 plasmabio-test 1237fbae7d24[23293]: [I 2022-03-29 07:02:14.887 SingleUserNotebookApp log:189] 302 GET /user/foo/ -> /user/foo/lab? (@1.2.3.4) 1.32ms
Mar 29 07:02:14 plasmabio-test 1237fbae7d24[23293]: [I 2022-03-29 07:02:14.923 SingleUserNotebookApp log:189] 302 GET /user/foo/lab -> /hub/api/oauth2/authorize?client_id=jupyterhub-user-foo&redirect_uri=%2Fuser%2Ffoo%2Foauth_callback&response_type=code&state=[secret] (@1.2.3.4>
Mar 29 07:02:15 plasmabio-test 1237fbae7d24[23293]: [I 2022-03-29 07:02:15.047 SingleUserNotebookApp auth:992] Logged-in user {'kind': 'user', 'name': 'foo', 'admin': True, 'groups': [], 'server': '/user/foo/', 'pending': None, 'created': '2022-03-29T06:43:56.625610Z', 'last_activit>
Mar 29 07:02:15 plasmabio-test 1237fbae7d24[23293]: [I 2022-03-29 07:02:15.048 SingleUserNotebookApp log:189] 302 GET /user/foo/oauth_callback?code=[secret]&state=[secret] -> /user/foo/lab (@1.2.3.4) 51.45ms
Mar 29 07:02:15 plasmabio-test 1237fbae7d24[23293]: [I 2022-03-29 07:02:15.913 SingleUserNotebookApp log:189] 200 GET /user/foo/api/kernelspecs?1648537335747 (foo@1.2.3.4) 114.00ms
Mar 29 07:02:15 plasmabio-test 1237fbae7d24[23293]: [I 2022-03-29 07:02:15.988 SingleUserNotebookApp log:189] 200 GET /user/foo/lab/api/settings?1648537335752 (foo@1.2.3.4) 72.87ms
Mar 29 07:02:15 plasmabio-test 1237fbae7d24[23293]: [I 2022-03-29 07:02:15.990 SingleUserNotebookApp log:189] 200 GET /user/foo/api/kernels?1648537335759 (foo@1.2.3.4) 70.30ms
Mar 29 07:02:15 plasmabio-test 1237fbae7d24[23293]: [I 2022-03-29 07:02:15.991 SingleUserNotebookApp log:189] 200 GET /user/foo/api/terminals?1648537335760 (foo@1.2.3.4) 71.07ms
Mar 29 07:02:15 plasmabio-test 1237fbae7d24[23293]: [I 2022-03-29 07:02:15.993 SingleUserNotebookApp log:189] 200 GET /user/foo/api/sessions?1648537335760 (foo@1.2.3.4) 2.67ms
Mar 29 07:02:15 plasmabio-test 1237fbae7d24[23293]: [I 2022-03-29 07:02:15.996 SingleUserNotebookApp log:189] 200 GET /user/foo/api/kernelspecs?1648537335922 (foo@1.2.3.4) 1.56ms
Note
Similar to the command above, you can also combine the -f and -n options:
sudo journalctl CONTAINER_NAME=jupyter-username- -f -n 1000
Why is my environment not building?#
If for some reasons an environment does not appear after Adding a new environment, it is possible that there are some issues building it and installing the dependencies.
We recommend building the environment either locally with repo2docker (next section) or on Binder.
See Testing on Binder and the repo2docker FAQ for more details.
Accessing the repo2docker container#
In Plasma, repo2docker runs in a Docker container, based on the Docker image available at
quay.io/jupyterhub/repo2docker:main.
If you are not able to run repo2docker manually to investigate a build failure (see section below), you can try to access the
logs of the Docker container.
On the machine running TLJH, run the docker ps command. The output should look like the following:
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
146b4d335215 quay.io/jupyterhub/repo2docker:main "/usr/local/bin/entr…" 31 seconds ago Up 30 seconds 52000/tcp naughty_thompson
You can then access the logs of the container with:
docker logs 146b4d335215
# or with the generated name
docker logs naughty_thompson
If the repo2docker container has stopped, then you can use the docker ps -a to display all the containers.
The output will show Exited as part of the STATUS:
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
146b4d335215 quay.io/jupyterhub/repo2docker:main "/usr/local/bin/entr…" 4 minutes ago Exited (0) About a m
Running the environments on my local machine#
To run the same environments on a local machine, you can use jupyter-repo2docker with the following parameters:
jupyter-repo2docker --ref a4edf334c6b4b16be3a184d0d6e8196137ee1b06 https://github.com/plasmabio/template-python
Update the parameters based on the image you would like to build.
This will create a Docker image and start it automatically once the build is complete.
Refer to the repo2docker documentation for more details.
My extension and / or dependency does not seem to be installed#
See the two previous sections to investigate why they are missing.
The logs might contain silent errors that did not cause the build to fail.
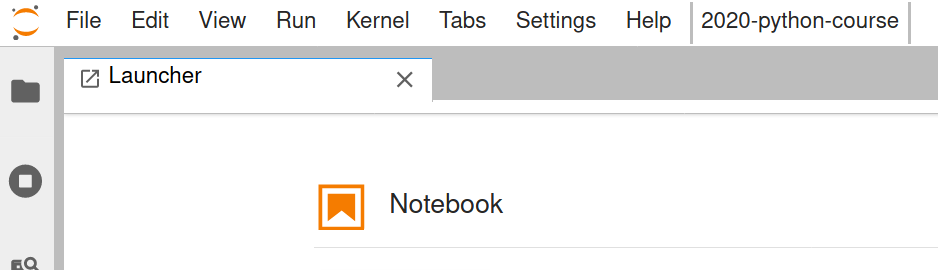
The name of the environment is not displayed in the top bar#
This functionality requires the jupyter-topbar-text extension to be installed in the environment.
This extension must be added to the postBuild file of the repository.
See this commit as an example.
The name of the environment will then be displayed as follows:
The environment is very slow to build#
Since the environments are built as Docker images, they can leverage the Docker cache to make the builds faster.
In some cases Docker will not be able to leverage the cache, for example when building a Python or R environment for the first time.
Another reason for the build to be slow could be the amount of dependencies specified in files such as environment.yml or
requirements.txt.
Check out the previous section for more info on how to troubleshoot it.
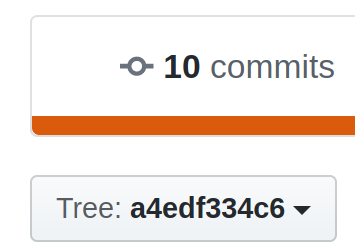
Finding the source for an environment#
If you are managing the environments, you can click on the Reference link in the UI,
which will open a new tab to the repository pointing the commit hash:
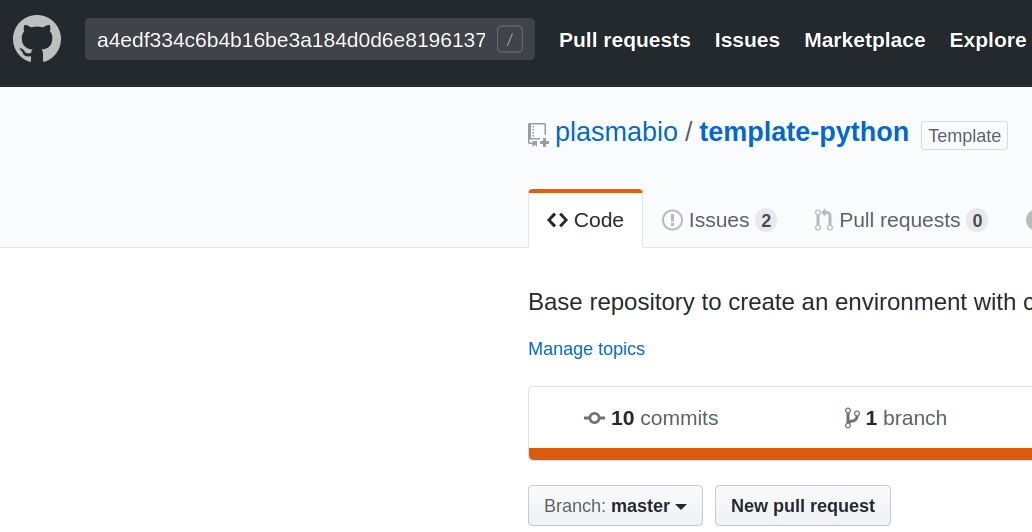
If you are using the environments, the name contains the information about the repository and the reference used to build the environment.
On the repository page, enter the reference in the search input box:
Removing an environment returns an error#
See Removing an environment returns an error for more info.
